Medical Checkup For Hypertensive Patients
Hypertension, more commonly known as high blood pressure, is a medical condition where the blood force against the artery walls is consistently too high, typically defined as a systolic pressure of 130 mm Hg or higher and/or a diastolic pressure of 80 mm Hg or higher. This elevated pressure can damage blood vessels and organs over time, significantly increasing the risk of serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and vision loss.
Hypertension can result from various factors, including genetics, poor diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and stress. It often develops without noticeable symptoms, earning it the nickname “the silent killer,” and requires regular monitoring and management through lifestyle changes, medication, and medical supervision to prevent complications.
In Cuba, a detailed checkup approach is carried out to ensure that all aspects of hypertension are thoroughly evaluated and managed. Based on the findings, a holistic and effective plan to control high blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications will be recommended.
Key Components of Hypertension Checkup
The hypertension checkup begins with a detailed review of the patient’s medical history and consultations with specialists.
- Consultations:
- Cardiologist: In-depth evaluation of heart health.
- Nephrologist: Assessment of kidney function to identify if there are any renal causes for hypertension.
- Endocrinologist: Hormonal evaluation to assessment if there are endocrine causes for the hypertension, such as thyroid disorders or adrenal gland abnormalities.
- Nutritionist/Dietitian: Recommendation for detailed dietary plans to support blood pressure management.
- Patient History:
- Personal Medical History Detailing: Previous diagnoses, treatments, and surgeries. Details on any known hypertension or cardiovascular diseases.
- Family History: Incidence of hypertension, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, or other related conditions in immediate family members.
- Symptoms: Current symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, chest pain, shortness of breath, or any other complaints.
- Lifestyle Factors: Detailed questions about diet, physical activity, smoking status, alcohol consumption, and any use of recreational drugs.
- Medication Use: Current and past use of prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements.
- Physical Examination:
- Vital Signs: Measurement of blood pressure (multiple readings), heart rate, temperature, and respiratory rate.
- Anthropometric Measurements: Height, weight, body mass index (BMI), and waist circumference.
- Cardiovascular Examination: Inspection, palpation, and auscultation of the heart. Checking for any signs of heart enlargement or abnormal heart sounds.
- Peripheral Vascular Examination: Checking for pulse quality, symmetry, and any signs of peripheral artery disease (e.g., weak pulses, swelling).
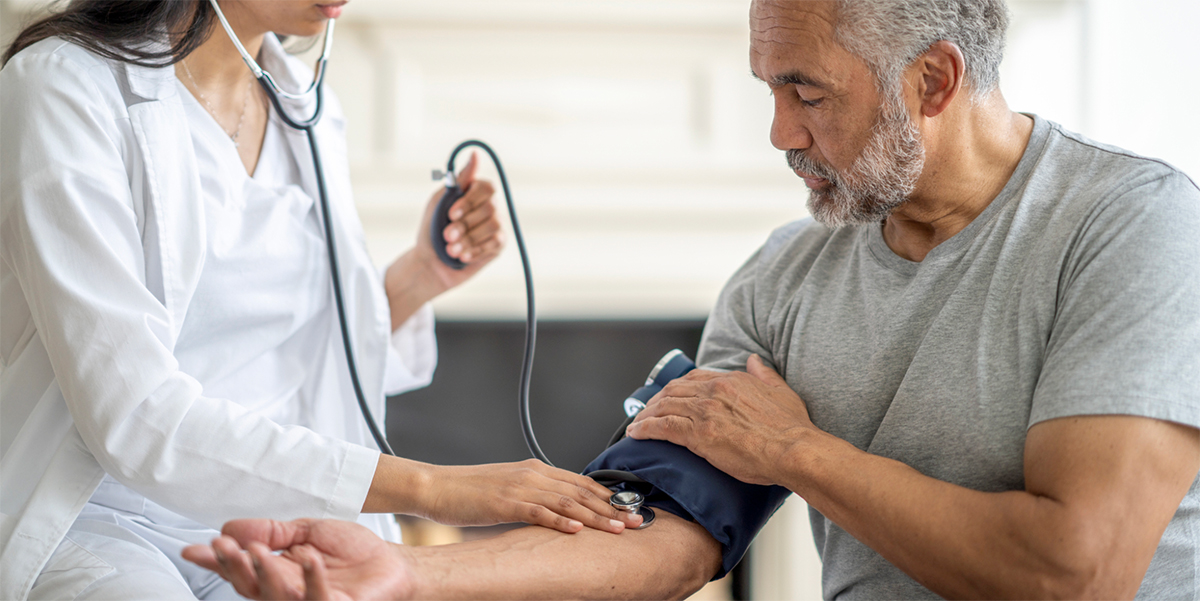
- Blood Pressure Measurement
- Standard Technique: Blood pressure measured with a properly calibrated and validated instrument, with the patient seated, back supported, feet flat on the floor, and arm supported at heart level. At least two readings taken one to two minutes apart and averaged.
- Positional Changes: Blood pressure readings taken in different positions (sitting, standing, and lying down) to assess for orthostatic hypotension or other anomalies.
- 24-hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM): A portable device worn by the patient that measures blood pressure at regular intervals over 24 hours, providing a comprehensive profile of blood pressure fluctuations during daily activities and sleep.
- Laboratory Tests
- Lipid Profile: Total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
- Blood Glucose: Fasting blood glucose, HbA1c for diabetes screening.
- Kidney Function Tests: Serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium).
- Thyroid Function Tests: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free T4, and possibly free T3.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Hemoglobin, hematocrit, white blood cell count, and platelets to check for anemia or other hematological conditions.
- Liver Function Tests: To assess liver health and rule out any hepatic causes of hypertension.
- Imaging and Diagnostic Tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To identify arrhythmias, signs of ischemia, or left ventricular hypertrophy.
- Echocardiogram: To evaluate heart structure and function, including the size of the chambers, the thickness of the heart walls, and the function of the heart valves.
- Carotid Ultrasound: To assess blood flow and detect plaque buildup.
- Renal Ultrasound: To evaluate the size, shape, and structure of the kidneys, looking for abnormalities that might contribute to hypertension.
- Chest X-ray: To check for heart enlargement, fluid in the lungs, and other signs of heart failure or pulmonary hypertension.
- Lifestyle and Risk Assessment
- Diet and Nutrition Evaluation: Detailed assessment of daily food intake, focusing on sodium, fat, and sugar consumption.
- Physical Activity Assessment: Evaluation of current physical activity levels, including type, frequency, duration, and intensity of exercise.
- Stress and Mental Health Evaluation: Assessment of stressors in the patient’s life, coping mechanisms, and overall mental health.
Based on the results of the above evaluations and tests, a tailored treatment and management plan is developed to help control blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications.
ACCOMMODATION:
Private room with the following features:
- Electronic patient bed
- Equipment for disabled patient
- Oxygen hookup
- Three AP meals taking into account the patient’s preferences and / or special diets prescribed by physician
- Fully equipped private bathroom
- Infirmary and nursing care
- Colour TV with national and international channels
- Local and international phone services (extra cost will apply)
- Safe box
- Internet service on every floor
- Laundry services
- Assistance in visa issuance and extension (If needs be)
- Each patient/ companion will be assigned a multi-lingual field member with the mandate of attending to all of our patients’ translation and personal needs;
- 20 hours internet service;
- Local airport pickup and drop off; and
- Hospital pickup and drop off (if needed)
